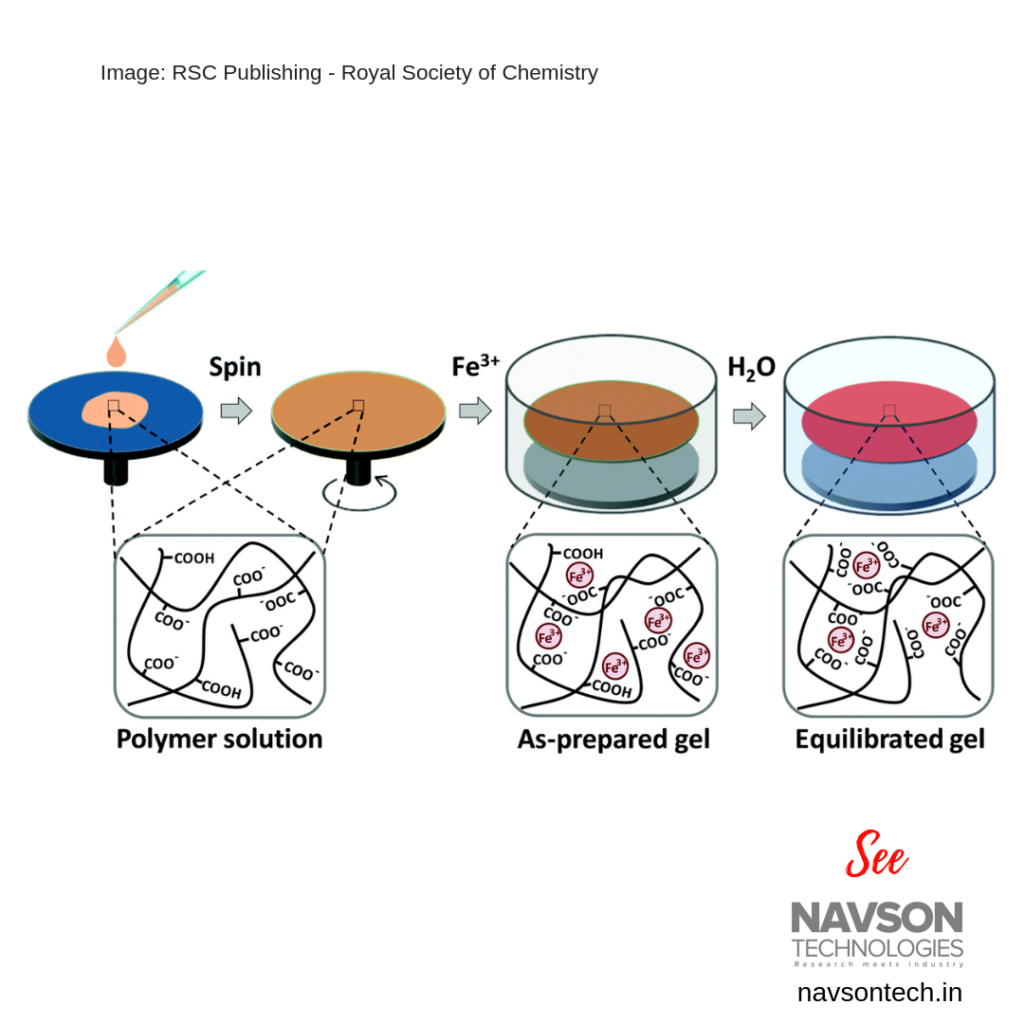
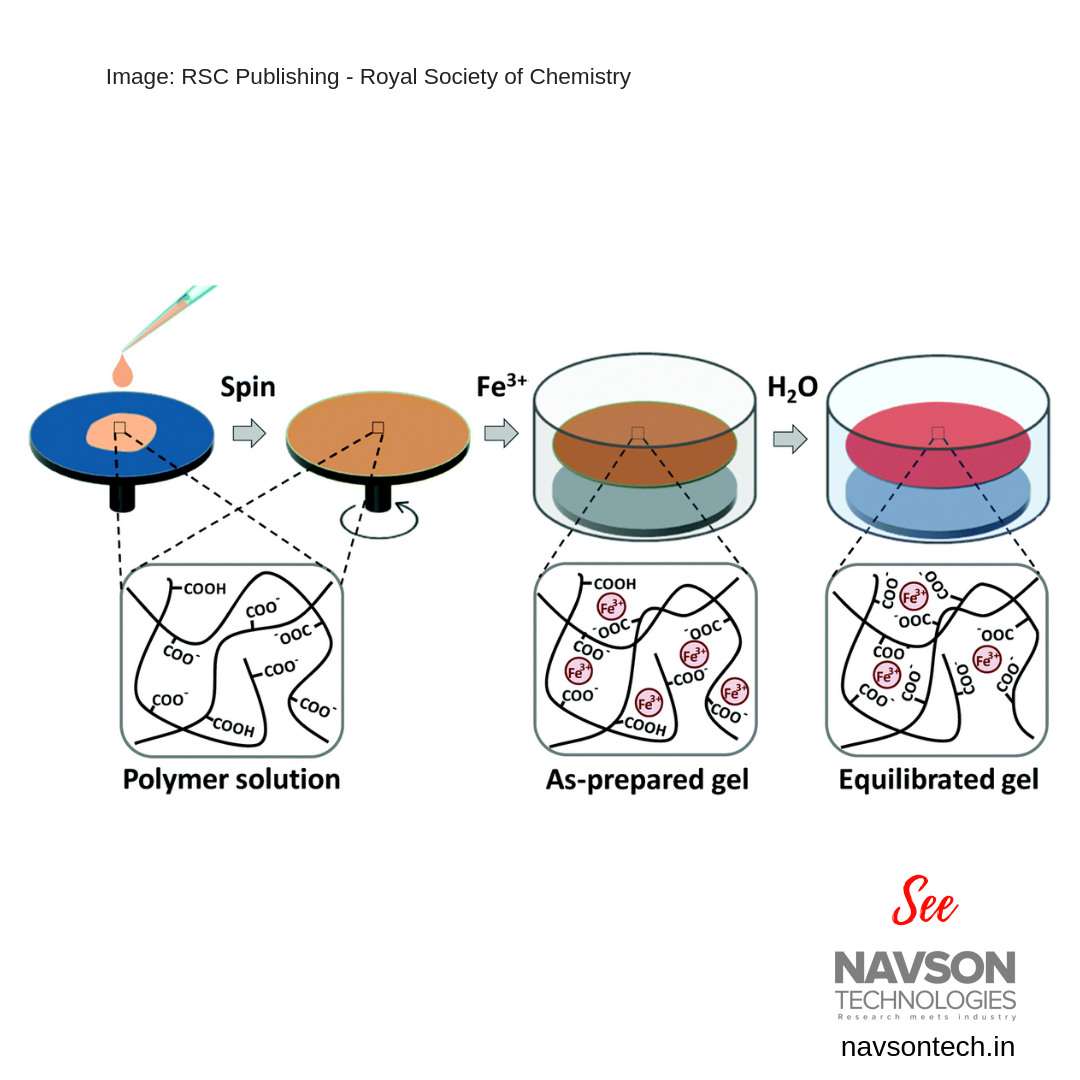
Thin hydrogel films have attracted great attention due to their promising applications in molecular separation, medical dressings, flexible electronics, etc. The tough physical hydrogel films by spin coating of a P (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) or P (AAc-co-NIPAm) polymer solution and a subsequent gelation process, in which robust carboxyl–Fe3+ coordination complexes
were formed.
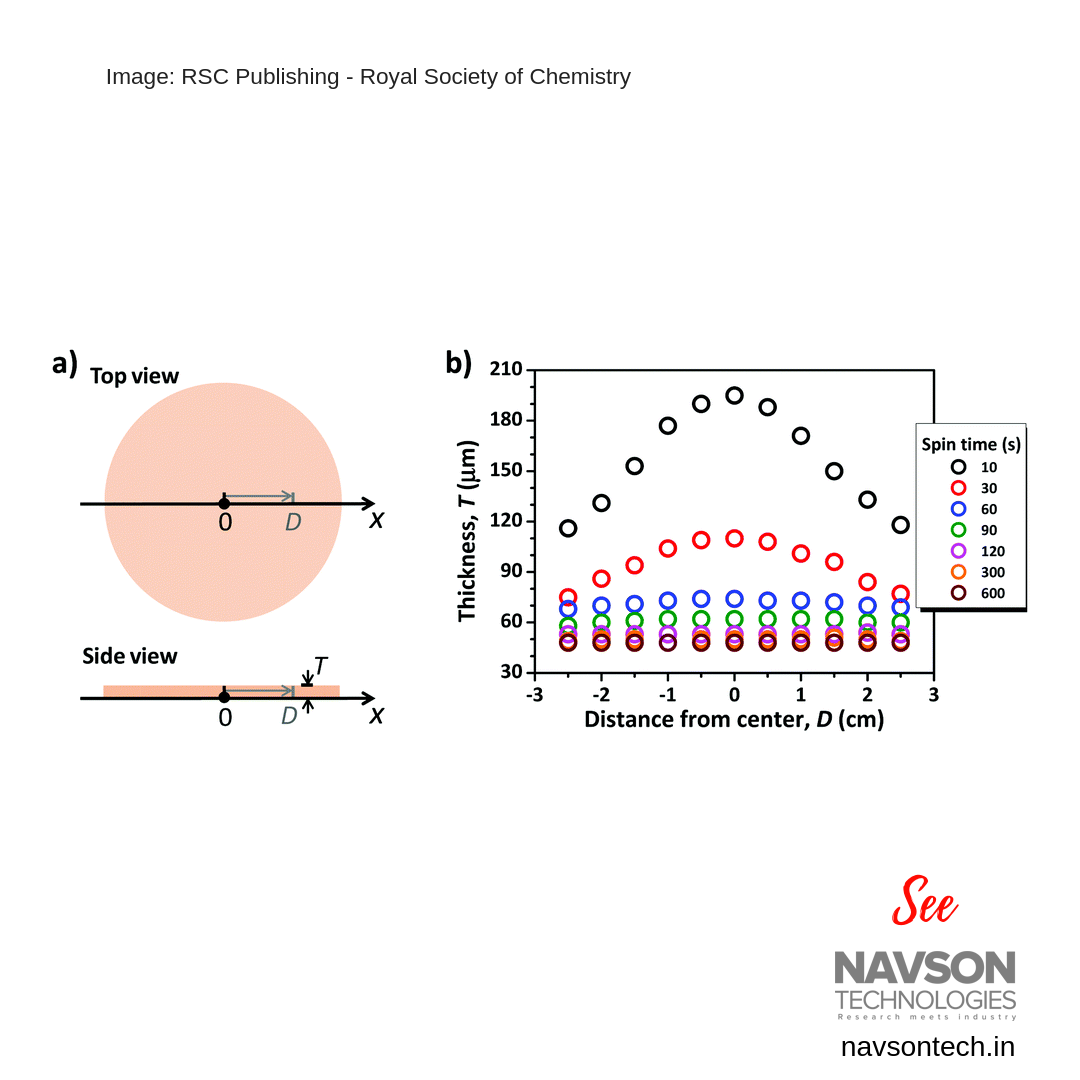
By controlling the spin time, spin speed, and concentration of the polymer solution, the thickness of the films could be well tuned, ranging from several to hundreds of micrometers. The hydrogel films showed excellent mechanical properties, with tensile breaking strengths, breaking strains, Young’s moduli and tearing fracture energies. The obtained gel films showed a fast response (<60 s) and a large output force (~0.2 MPa) triggered by a concentrated saline solution, making them an ideal material in the design of chemomechanical device.
Reference: DOI: 10.1039/c8sm01126e